Banking

Digital BAnking -CBDC
A Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) is the digital form of a country's fiat currency, issued and regulated by its central bank. It is a direct liability of the central bank, making it a risk-free form of digital money, distinct from the commercial bank deposits that underpin current digital banking services.
Key Characteristics
-
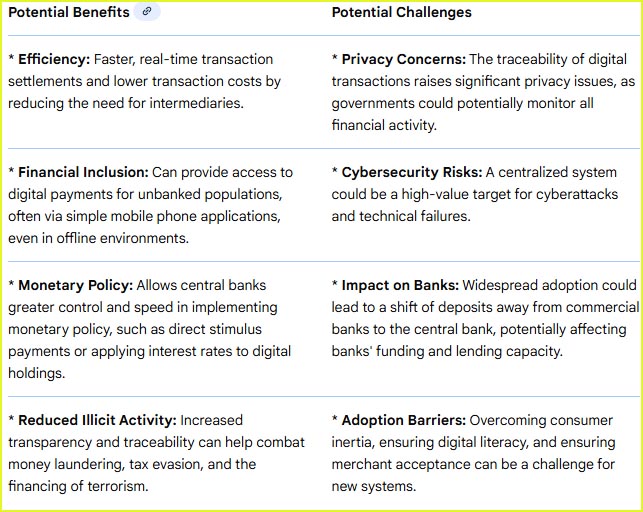
The introduction of a CBDC is a major evolution within digital banking. While most current "digital money" consists of commercial bank liabilities transferred through systems like UPI, NEFT, or card networks, a CBDC provides a public, central bank-backed alternative. Commercial banks play a crucial role in the distribution of retail CBDCs. In many pilot programs (China such as digital yuan or e-CNY), central banks issue the digital currency to commercial banks, which then distribute it to customers through dedicated digital wallets and mobile apps. Over 130 countries, representing 98% of the global GDP, are exploring a CBDC. The Bahamas, Jamaica, and Nigeria have fully launched retail CBDCs, while major economies like China (digital yuan), India (digital rupee), and the European Union (digital euro) are running advanced pilot programs. The US Federal Reserve is actively researching the potential for a digital dollar but has not made a decision to issue one yet.
1. Retail CBDC (CBDC-R): Designed for use by the general public for everyday transactions, similar to digital cash in a mobile wallet.Relation to Digital Banking
Global Status
